Evaluating Customer Churn Risk
The use of a customer health score is a common approach to assessing customer risk and then defining a set of ranges in the score that define the customer risk as Red, Yellow or Green state of the customer health.
However, the challenge with this approach is understanding WHY the customer has this score and what were the causes. It is difficult to put the right plan in place to help customers get from a Red or Yellow state to the Green state without understanding the WHY.
I developed this Risk Analysis approach due to finding trends in the customer data that were more highly correlated to customers who ended up churning. I defined these common four quadrants based on the common attributes that were associated with different levels of engagement versus indispensability.
The goal of any SaaS company is to have at least 95% of their customers in the Green quadrant. In order to put a plan in place each year to drive customers into the Green quadrant, you have to start by assessing all of your customers into one of these quadrants based on the attributes that define each risk state.
How many of your customers are in each of the following quadrants? Do you collect the customer data to determine which category each of your customers are in? If not, I would encourage you to begin collecting and tracking this type of data that will bring more clarity into the WHY your customers are at risk.
The following Customer Risk Analysis Assessment model is what I use to categorize the entire customer base into each of these quadrants.
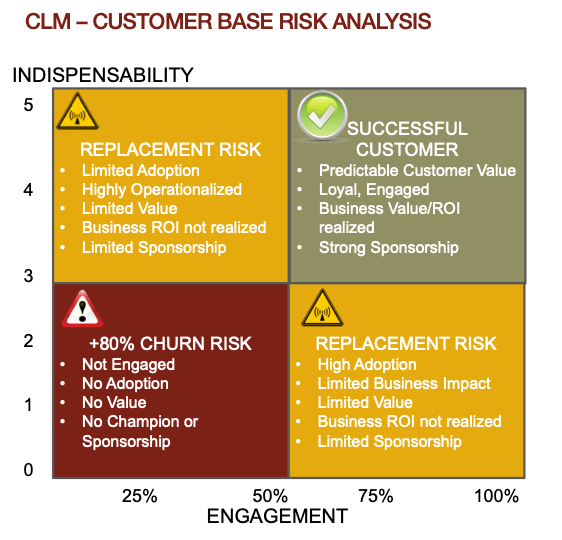
Why is it important to understand the risk in your customer base as it relates to the Red, Yellow and Green quadrants above? This analysis is the key to enabling the CSM team to build the right plays for customers in the Red and Yellow categories to deliver a plan that helps the customers get in the Green quadrant and stay there.
Customer Risk Assessment Definition
Let’s break down each of the quadrants and define what attributes determine the risk for customers.
There are two main business impact categories that are important to establish with each customer to achieve real business impact and ROI.
Indispensability
Indispensability is the ability for the solution to become indispensable to the company by innovating critical operations. It entails the technology being used in the daily operations of the company within critical business processes. These tend to be process improvements that drive efficiencies, effectiveness and innovations that lowers costs and/or drives revenue streams. Indispensability also requires the solution to drive long term ROI, not just a one time savings or short term innovation.
Engagement
Engagement is the usage of the solution by the user community. It entails how many different areas of the product are used and the number of users that actively use the solution to help them do their job better. If the solution usage radiates based on growth in a different unit of measure besides users, then the engagement factor is based on how this unit of measure grows over time to consider the solution being used to the maximum capacity of the customer capability.
When assessing the customer risk, these two areas are the key to understanding how entrenched your solution is within the company and across organizations or business units.
Using Workfront as an example, if the customer has 2500 users using Workfront to track time, but they haven’t started using the solution to track and manage projects or work tasks within a specific area like Marketing, IT or PMO office. This customer would have a higher Engagement score due to the number of users across the company using Workfront every day to track time. However, they would have a low Indispensability score because they are only using the solution for one process. The Risk would be in the Replacement quadrant due to the fact that there are many time tracking solution on the market that could easily replace Workfront.
Risk Assessment by Quadrant
Replacement Risk Quadrants
There are two Replacement Risk Quadrants which we would consider a customer with risk for churn due to the ease of which the customer could replace the solution with another that has similar capabilities. These are customers that would require a plan to be put in place to help them expand their usage of the solution to either be used in more critical business processes or rolled out to more users across the organizations or business units.
The upper left quadrant is the Replacement Risk quadrant whereby the customer is using the solution in one small department or area of the company for several critical business processes. The solution is being used in a higher indispensable manner and making an impact to the business, but perhaps in a small group and not across a large enough organization to create a higher ROI to warrant a renewal or expansion. The solution is still at risk to be replaced by another solution if a CXO comes in and wants to standardize across the company on one solution. The attributes used to evaluate this type of risk are:
Limited Adoption by a few Users or Champions using it for several use cases
Highly Operationalized in one team, department or small business unit for several critical or impactful business processes on a daily/weekly or monthly basis
Limited Value has been acknowledge or confirmed by the customer
Business ROI and Impact has not been fully proven or realized by the customer enough to commit to expanding
Limited Sponsorship by the executive leadership team. The key sponsor or economic buyer has not been engaged to support the customer team and the commitment to engagement across the organization or other business units
The lower right quadrant is the Replacement Risk quadrant whereby the customer is using the solution across a large department, organization or business unit but only for one business process. It will have less risk if that one business process is critical to the business as it will score a bit higher in the Indispensability factor, but the risk will still be that the a CXO could choose another competitor solution that can be used for additional critical business processes and create a higher business ROI. The attributes used to evaluate this type of risk are:
High Adoption by many users across a business unit or organization
Limited Business Impact to the business unit and company due to the process the solution is being used for is of low value and not critical to the business
Limited business value has been realized due to making some processes easier or more digital, but perhaps not enough to create an ROI.
Business ROI and Impact has not been fully proven or realized by the customer enough to commit to expanding
Limited Sponsorship by the executive leadership team. The key sponsor or economic buyer has not been engaged to support the customer team and the commitment to engagement across the organization or other business units
The Churn Risk Quadrant
The lower left quadrant is the Churn Risk quadrant due to the assessment that the customer is either not using the solution at all or is only using the solution in a minimalistic manner. It is usually a customer who only have a few users using the solution for only one or two non critical business processes. The usage is all in the low value areas of the operations. The customer leadership could view the solution as a nice to have but clearly not making a significant enough impact to the business and does not provide enough value or ROI to consider continuing their investment in the solution.
The Successful Customer Quadrant
The upper right quadrant is the Successful Customer quadrant and the utopia we are driving all the customers towards with each solution plan. These are customers who are using the solution in several critical business processes where they are able to confirm the realization of a business impact and ROI. Due to the business impact they have realized, they are using the solution across several departments, business units and organizations to continue to drive business ROI long term. They are willing to refer the solution to other colleagues and companies as well as be references including doing videos testimonies and case studies.
Evaluating and Assessing Risk for the entire customer base
With the understanding of these definitions, this is how I suggest the CS leadership evaluate the entire customer base. They would spend some time using the customer data to review what percentage of your customer base falls into each of these quadrants.
To begin; use the list of attributes above and align the attributes to the Customer KPIs and metrics that are being tracked for both software usage and business impact.
Here is an example of metrics associated with the attributes
Attribute | Metrics | Tracking |
|---|---|---|
Adoption | Product Usage stats | Create ranges for each usage stat to define low, medium and High usage status |
Operationalization | Product Usage of specific elements of the product Business Process Definition of Future State in Production User Community | Create ranges for each usage stat to define low, medium and High usage status New business workflow(s) configured, tested and in Production Customer confirms all users in Production. Product Usage stats confirm activity |
Business Value and Impact | Set of Customer Goals Business Outcomes | Confirmed in Business Value Review |
Key Sponsor(s) | Documented Name, Role and contact information | Responsiveness to emails and calls Attends Monthly/Quarterly Exec Reviews Attends Quarterly and/or Annual Strategy meetings |
These elements can all be tracked in a Customer Database and utilized in the health score algorithms as well as Business Value Realization assessments.
As long as your health score range definitions include the confirmation of the business entrenchment and value impact and ROI, then the playbooks for the various plays can be defined accordingly.
I suggest conducting the Customer base risk assessment for each market segment or target market.
Here is an example of how I would present and review this assessment to the executive leadership team and board:
Starting with the Summary Report of All Customers in the base:

This summary report is highlighting a 12% churn risk which stands out due to a churn goal of 5%. It also is showing 40% of the base is at risk to be a potential churn in revenue or logo when you add both Replacement Risk quadrants. This would tell the CS team that 52% of the customer base needs a plan on how to get customers from where they are today to the vision of how to operationalize the solution both deep and wide throughout their company.
The next question that comes to mind is “Which market segment is driving the churn or at risk trends?” As we drill down on the customer base analysis into each of the market segment, it will help us to understand if there is a particular market segment that is driving the higher churn and replacement risk categories. For this example, we will use the common market segments of Enterprise and Mid Market.
Reviewing the Market Segment: Enterprise:

In reviewing the above chart showing the Enterprise market segment, the report indicates that there is a high success rate and a low churn rate with some risk in the replacement category. This may also only represent a few customers depending on what the customer count is for the Enterprise segment. However, this would not be the segment that is driving the higher churn rate but is contributing to the replacement risk levels.
Reviewing the Market Segment: Mid Market

In reviewing the above chart for the Mid Market segment, the report indicates that there is a much lower success rate and a very high churn rate with high risk in the replacement category. Depending on the customer counts associated with each of these market segments, I would be concerned that the Mid Market segment is struggling to understand how to operationalize the solution. It would also indicate that the right ICP has not been identified correctly in this market segment. The chart is clearly showing this segment as the one driving the higher churn rate and contributing to the replacement risk levels.
The Customer Base risk analysis will provide the leadership team with the overall understanding of the customers and revenue at risk and which segments are realizing more success with the solution. The drill down reporting will help to understand which segments may be having more challenges in getting to a Success state. From there a more detailed analysis can be done within the segment to understand if the customers at risk are outside your ICP. If ICP customers are falling into the risk quadrants, then more detailed analysis should be conducted to understand what is causing the risks.
The Next Level of Risk Assessment
In drilling down on the customer analysis within a segment, there are specific areas that will provide additional insights into what is causing the risk and deteriorating the customers confidence in the solution. The following are the key customer management elements that affect risk:
Customer team commitment level
Implementation Plan execution issues
Product Bugs or issues logged
Business Value Outcomes are not associated with critical business operations
ROI calculation cannot be determined
Evaluating each of these elements of the customer engagement and experience with the solution, implementation and support will provide the insights the CSM can use to assess any trends and areas that require modifications or course correction with the CLM approach. During the customer meetings, the CSM can ask more specific questions within each of these areas to understand the customer’s perception of which of these may be degrading their confidence in the solution to provide the expected business impact.
In summary, the CS team will be able to be more strategic in creating their customer plans to drive all of their customers to the Green state of realizing value and ROI if they can complete this risk assessment each quarter. This analysis will provide CSMs with a map of the customers that require either a modification to their current plan or and entirely new plan that will drive the customer to the promise land of realizing business value impact and ROI.


